Arrays
When a program needs lots of variables, declaring each one individually can be time-consuming and makes the code messy. To solve this problem, we can use arrays, which lets us group related data together.
What is an Array
An array is a series of variables of the same type and fixed size that are stored sequentially and share a common name. Variables in an array are called elements.
To differentiate between the elements in the array, each element is assigned a number (also called index). For an array of n elements, the elements are indexed sequentially from 0 to n - 1.
Declaring Arrays
To declare an array the following syntax is used:
type name[size];Where:
type: The type of all elements in the array.name: The name which will be used to address the array.size: The number of elements in the array.
For example:
int a[4];This defines an array named a[] with size 4. The size of the array can’t change after the initialization.
The size of an array doesn’t have to be an explicit integer, it can be an expression which let us choose the size of the array based on the current state of the programm.
int n ;
cin >> n;
int a[n + 1]; // makes an array of size n + 1Initializing
If an array is defined locally we know that all elements in a[] have undetermined values. To give an array initial values, we can do the following:
int a[4] = {2 , 4 , 5 , 0};This will make an array that looks like as in the picture, where the cells are the elements of the array and the numbers below are the indices:
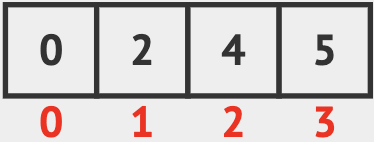
To decalre an array locally, and let all of its elements be 0, we can write:
int a[2000] = {};This will make 2000 integers each with inital value equal to 0.
Accessing Elements
To call an element in the array the following syntax is used:
name[index];Where:
name: The name of the array.index: The index of the element that’s called.
That elements in an array act like regular variabes. The following code shows an example for this.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // value 1 is assigned to a[0]
int x = a[0]; // x will be equal to 1
a[0]++; // a[0] will become 2
cout << x << endl; // printing 1
cout << a[0] << endl; // printing 2
}Examples of Using Arrays
Looping over Arrays
We can make a loop that moves through the whole array by looping over its indices (0 to array_size - 1). Let’s say we want to find the sum of an array.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int n;
cin >> n; // read the size of the array
int a[n]; // make an array of size n
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // loop through all the indices, from 0 to n - 1
cin >> a[i]; // for each index i, read the value of a[i] from the input
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
sum += a[i]; // for each index i, add the value a[i] to sum
}
cout << sum << endl;
}Multidimensional arrays
Multidimensional arrays can be described as arrays-of-arrays, that is, an array in which each element in the array is an array as well. We call each level in the array a dimension. Let’s look at the following code.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int a[5];
int b[5][4];
}In this code:
a: A regular array of 5 integers.b: A two-dimensional array, that is, an array of 5 arrays each made of 4 integers.
Note that a[0] is an integer, and b[0] is an array of 4 integers.
To address an element in a multidimensional array we must specify the index of each dimension. To address an element in a we’ll write a[i], and for b we’ll write b[i][j].
Let’s say that we put some numbers in the cells of b, we can visualize the two-dimensional array as follows. 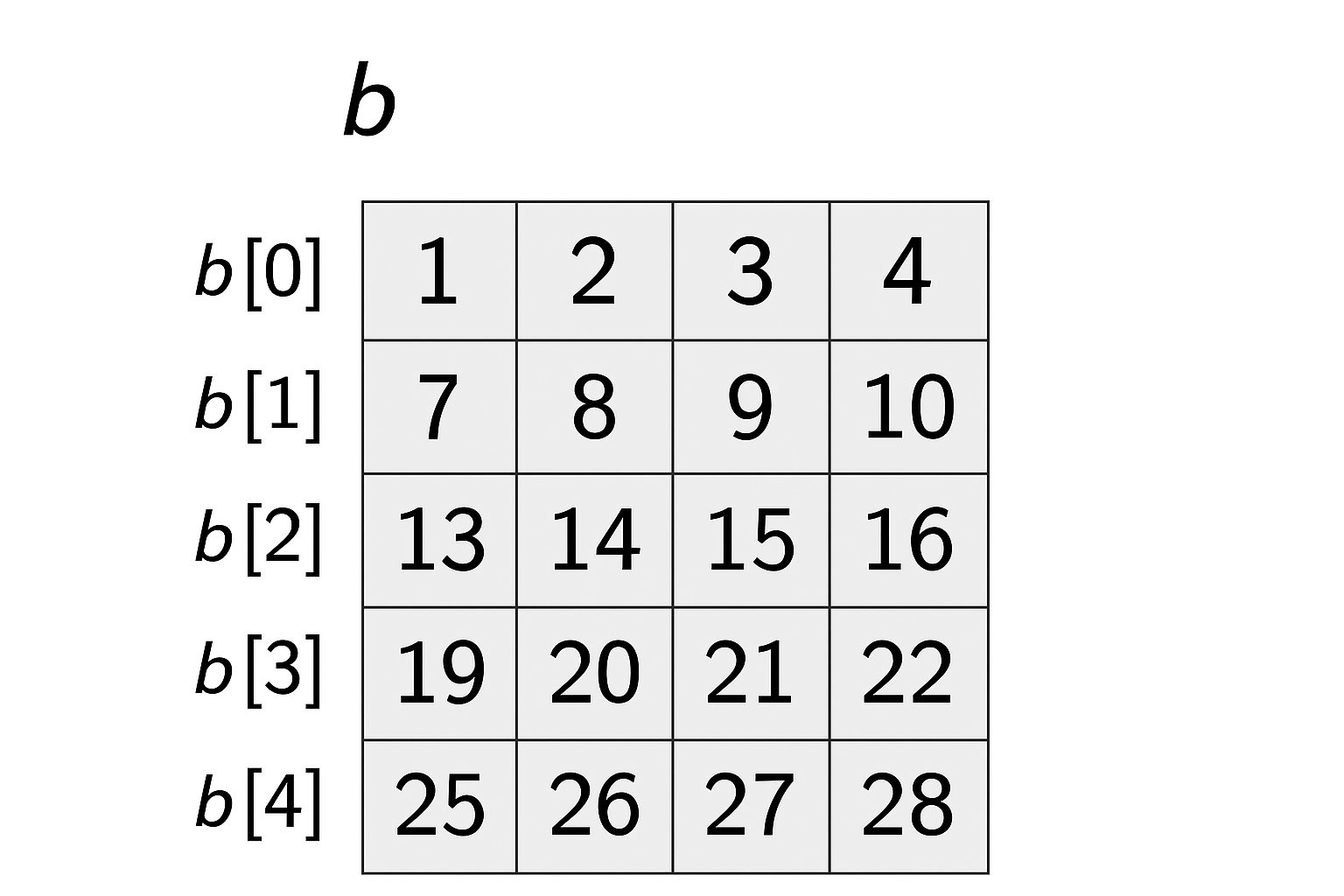
Here we can notice that b[0] is an array of 4 integers, and b[2][1] is a number 14.
Notice that when making a multidimensional array the number of cells will be the product of all dimensions lengths. In our example, b will have \(5*4 = 20\) cells.
The number of dimension in an array can be very high. We can make an array of 7 dimensions like int c[4][6][7][54][32][2][7] and even more.